Introduction
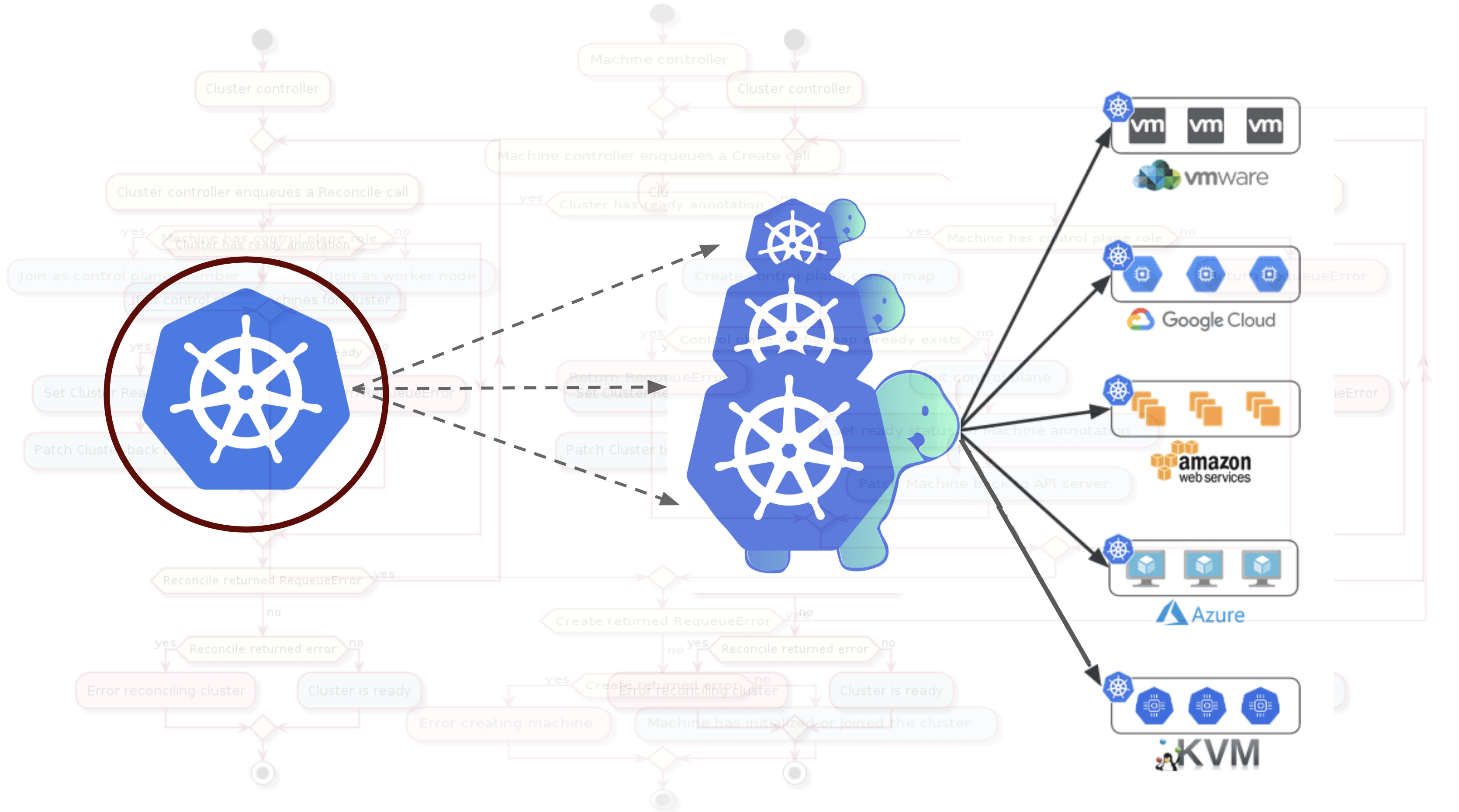
In the dynamic landscape of container orchestration, Kubernetes stands tall as the go-to solution for managing containerized applications seamlessly. To unlock its full potential, one must grasp the 10 key components that form the backbone of Kubernetes clusters.
1. Master Node: The Brainpower
The Master Node: Orchestrating the Symphony
At the core of every Kubernetes cluster is the Master Node. Serving as the orchestrator, it dictates the entire cluster’s functioning, coordinating tasks and managing resources efficiently.
2. Nodes: The Workforce
Nodes in Action: Where the Magic Happens
Nodes are the diligent workers in the Kubernetes ensemble. These entities execute tasks assigned by the Master Node, ensuring the smooth operation of applications within the cluster.
3. Pods: The Basic Building Blocks
Pods Unleashed: Containers in Harmony
Pods, the smallest deployable units in Kubernetes, encapsulate containers that work in tandem. They share the same network, storage, and have the ability to communicate, creating a cohesive environment.
4. Deployments: Strategic Application Management
Strategizing with Deployments: Streamlined Updates
Deployments facilitate the management of application updates and rollbacks. With automated processes, they ensure seamless transitions and maintain a stable environment.
5. Services: Exposing Functionality
Service Excellence: Connecting Applications
Services act as the bridge, enabling communication between different pods. They expose functionalities and ensure the smooth flow of data within the Kubernetes cluster.
6. Replication Controllers: Ensuring Stability
Controller of Stability: Managing Replica Sets
Replication Controllers guarantee the desired number of pod replicas, ensuring stability and availability. They play a pivotal role in maintaining the desired state of the cluster.
7. Labels: Organizing Chaos
Labeling for Order: Streamlining Resources
Labels provide an effective way to organize and select resources within a Kubernetes cluster. They act as key identifiers, simplifying the management of various components.
8. ConfigMaps: Configuration at Scale
Configuring at Scale: Streamlined Settings
ConfigMaps separate configuration details from application code, allowing for scalable management. They enhance flexibility and ease of configuration in dynamic environments.
9. Secrets: Safeguarding Sensitive Data
Secrets secure sensitive data, such as API keys and passwords, by providing a secure means of distribution within the Kubernetes cluster. A crucial element in maintaining a secure environment.
10. Persistent Volumes: Enduring Storage
Persistent Volumes offer a robust solution for persistent storage needs. They outlive pod lifecycles, ensuring data persists even when pods are terminated or rescheduled.
Conclusion
In the realm of Kubernetes clusters, understanding these 10 key components is akin to wielding a powerful toolkit. From the orchestration prowess of Master Nodes to the enduring storage capability of Persistent Volumes, each element plays a vital role in crafting a resilient and efficient Kubernetes ecosystem. Embrace the power of these components, and watch your containerized applications thrive in the dynamic digital landscape.