Algorithmic risk management has become a critical priority for enterprises as artificial intelligence increasingly drives business decisions. In 2026, organizations are no longer asking whether to use AI, they are asking how to control it responsibly while minimizing operational, legal, and ethical risks.
This is where algorithmic risk management comes in. It refers to the frameworks, policies, and systems enterprises use to identify, monitor, and mitigate risks arising from automated decision-making systems.
Why Algorithmic Risk Is Now a Business Issue
Algorithms now influence:
- Credit approvals
- Hiring decisions
- Fraud detection
- Customer personalization
- Financial forecasting
When these systems fail, the consequences are no longer technical, they are legal, financial, and reputational.
Enterprises face risks such as:
- Bias and discrimination
- Lack of transparency
- Regulatory violations
- Data misuse
- Unintended automation errors
As a result, algorithmic risk has moved from IT departments to executive leadership.
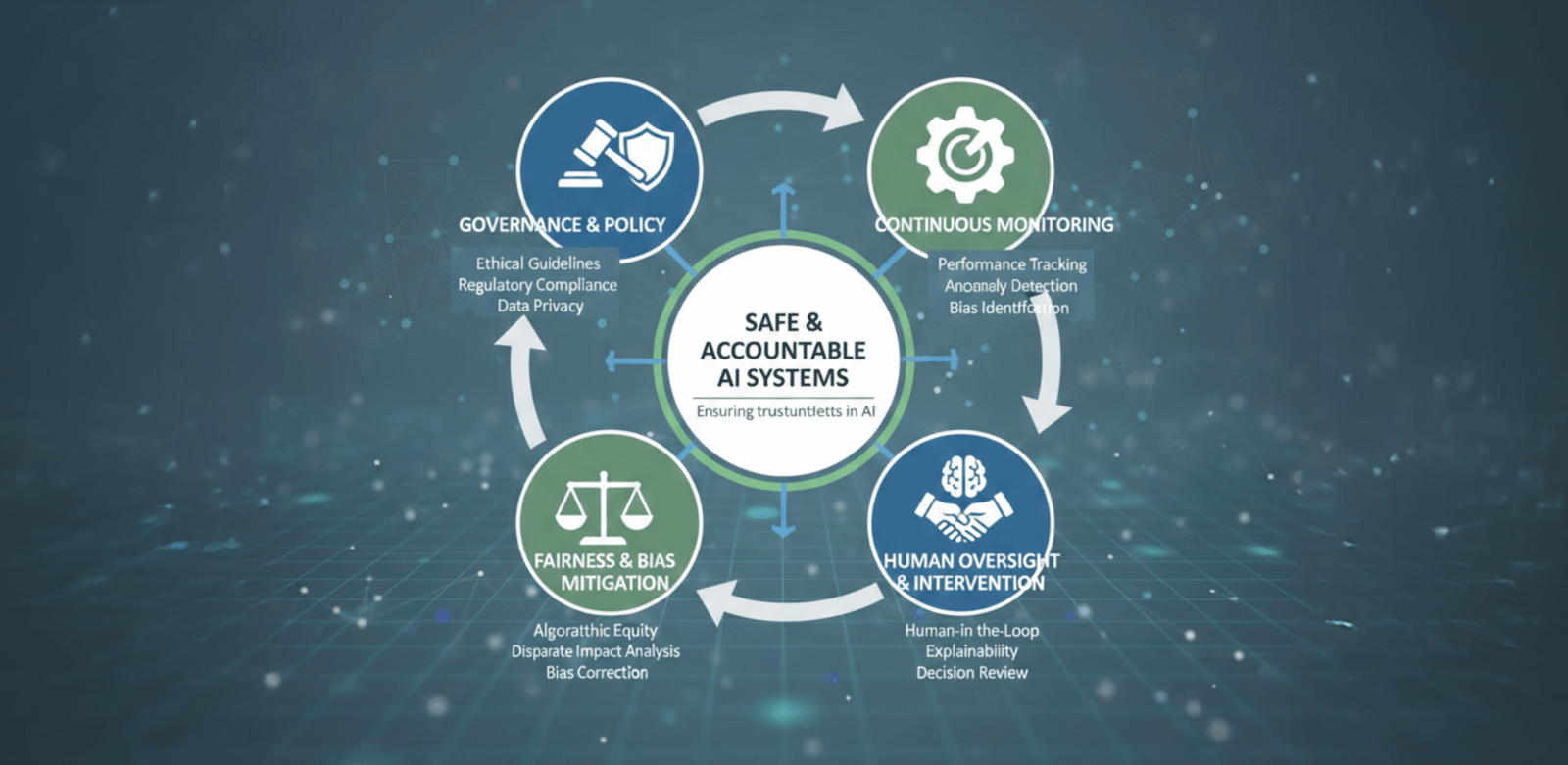
What Is Algorithmic Risk Management?
Algorithmic risk management is the discipline of ensuring that AI and automated systems operate within defined ethical, legal, and operational boundaries.
It includes:
- Model governance frameworks
- Continuous monitoring of algorithm performance
- Bias detection and correction
- Explainability mechanisms
- Human-in-the-loop controls
The goal is not to slow innovation, but to ensure trustworthy automation at scale.
Key Drivers Behind Algorithmic Risk Management in 2026
Several forces are accelerating its adoption:
1. Global AI Regulations
Governments are introducing AI-specific regulations focused on transparency, fairness, and accountability.
2. Enterprise AI Scale
Organizations now deploy hundreds of models across departments, making manual oversight impossible.
3. Reputational Risk
Public trust in AI systems directly impacts brand value and customer loyalty.
4. Legal Liability
Automated decisions increasingly fall under legal scrutiny.
The Core Components of an Algorithmic Risk Framework
Successful enterprises typically implement five pillars:
Governance
Clear ownership of AI systems, including approval processes and accountability structures.
Transparency
Explainable models that allow stakeholders to understand how decisions are made.
Monitoring
Real-time tracking of model behavior and performance drift.
Fairness
Bias audits to ensure equitable outcomes across demographics.
Human Oversight
Critical decisions still require human validation.
How Leading Enterprises Apply Algorithmic Risk Management
In practice, algorithmic risk management is not just a policy document. It is embedded into daily operations.
Enterprises apply it by:
- Establishing AI ethics committees
- Conducting regular algorithm audits
- Using model documentation standards
- Training employees on responsible AI usage
- Integrating risk dashboards into leadership reporting
This transforms AI governance from theory into operational reality.
Common Mistakes Organizations Still Make
Despite growing awareness, many companies still struggle.
Typical mistakes include:
- Treating AI risk as only a compliance issue
- Relying on one-time audits instead of continuous monitoring
- Ignoring explainability
- Deploying models without business accountability
- Focusing on speed instead of control
These gaps expose organizations to regulatory penalties and reputational damage.
The Strategic Value of Algorithmic Risk Management
Beyond compliance, algorithmic risk management creates a competitive advantage.
It enables:
- Safer AI adoption
- Faster enterprise scaling
- Higher customer trust
- Stronger regulatory readiness
- Sustainable innovation
In 2026, responsible AI is not a cost center, it is a growth enabler.
The Future of Algorithmic Governance
Looking ahead, this will become a standard enterprise function, similar to cybersecurity or financial risk management.
Future trends include:
- AI risk officers
- Automated risk scoring systems
- Real-time compliance engines
- Cross-border AI governance standards
Organizations that invest early will adapt faster and avoid crisis-driven reforms.
Conclusion
Algorithmic risk management represents the next evolution of enterprise governance. As AI systems increasingly shape business outcomes, organizations must move beyond blind automation and embrace structured oversight.
The enterprises that succeed in 2026 will not be those with the most AI, but those with the most trusted AI. Managing algorithmic risk is no longer optional; it is foundational to sustainable digital transformation.